So, you want to bring a Greyhound into your family? I’m sure you’ve already considered their appearance, temperament, and cuddleability and how they would fit into your family. But something that can be overlooked is Greyhound Anatomy: their health and body. It’s important to understand how they work physically and to learn about potential health issues that can occur throughout their lives.
Greyhound Anatomy
Greyhounds have been selectively bred for hundreds of years to be the best coursers, so many of their traits differ widely from other dog breeds. Greyhounds are easily identifiable by their long faces and thick necks, their streamlined muscular Greyhound bodies super narrow waists.
They also have long, thin legs and a flexible spine, which helps them to maintain their speed and manoeuvrability. Alongside these, they also have many internal differences making them unique to other dog breeds.
Make sure to find a vet aware of their differences so they can receive the best care at all times. Some of these differences can cause concern for an inexperienced Greyhound vet.
Greyhound Anatomy Chart: Unique Factors
Skull
A key trait of Greyhounds is their long face. This skull shape is called Dolichocephalic. This means they have a much bigger nasal cavity that helps them take in much bigger breaths and greatly benefits them when working or running around. Unlike the other extreme skull type found in flat-faced dogs, a Greyhound skull does not cause any health issues.
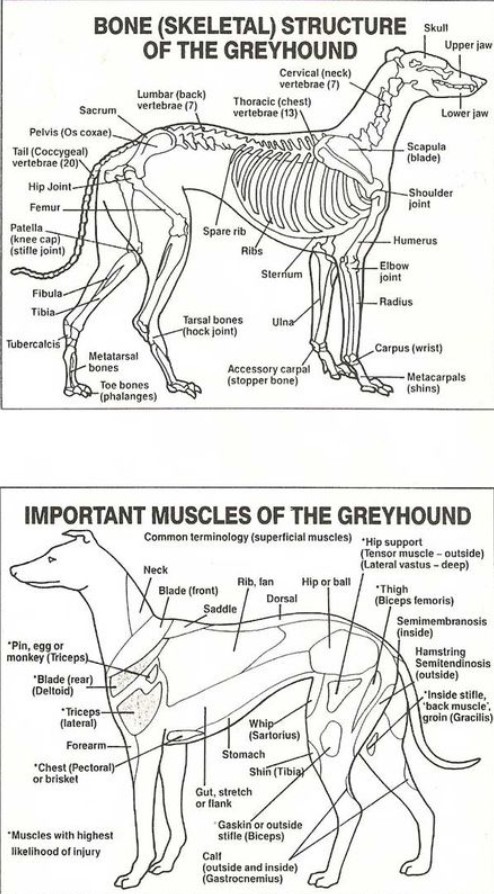
Skeletal Structure
Greyhounds are also known for their unique skeletal structure. They have a particular type of bone called a “carpus,” different from other breeds. It allows them to extend their legs further and more quickly than other dogs. This gives them a longer stride and enables them to run faster.
Blood
Greyhounds have a higher red blood cell count to help them transport more oxygen around their body and keep them running faster for longer. This makes them one of the most desirable breeds for blood donors! On average, they also have a lower white blood cell count as well.
Heart
A Greyhound’s heart is much larger than most dog breeds. It is almost equal to the size of a human heart! This is so they are better able to pump blood around their body while running, and often their blood pressure can appear higher than most breeds, but this is completely normal for them.
Lung Capacity
Another unique feature of greyhounds is their large lung capacity. This allows them to take in more oxygen when running, which helps them maintain their speed for more extended periods. Their heart is also unique and proportionally more prominent than other breeds, enabling them to pump more blood to their muscles.

Low Body Fat and High Muscle Mass
When we think of Greyhounds, almost everyone’s minds first think of how incredibly muscular their body is. Their extraordinary bulk is a result of selective breeding and their long history of working. They are also found to have increased creatine levels in their body. This contributes to their leanness and ability to develop and maintain muscle.
In balance with their high muscle mass, a typical Greyhound would have less than 2% body fat, making them one of the leanest breeds to ever exist.
Small Stomachs
Greyhound organs are often reduced in size due to their slim stature. To help maintain the low-fat percentage, Greyhounds have much smaller stomachs than most breeds, and often need to eat smaller meals but more frequently to help them get the correct nutrients but not cause digestive issues.
Sensitive to Anaesthesia
Due to their low body fat percentage, Greyhounds are much more sensitive to anesthetics. So, if your Greyhound is due for surgery, make sure to discuss anesthetic options with your vet to ensure the procedure goes as smoothly as possible.

Why are Greyhounds so Fast?
In addition to the Greyhound anatomy-related factors mentioned above, one of the reasons why greyhounds are so fast is their powerful hindquarters.
Their hindquarters are powerful and well-muscled, which gives them a powerful push off the ground. This allows them to reach high speeds quickly and maintain that speed for extended periods.
Greyhound Lifespan
Greyhounds typically are able to live long and healthy lives, and often easily live to 12-13 years old with minimal health issues. They could even push on for years longer! Luckily, this breed doesn’t have an increased risk of any degenerative diseases, so they are set to remain in good condition well into elderhood as long as they are loved and cared for correctly.
What is the Typical Cause of Death in Greyhounds?
Sadly, the leading cause of death in Greyhounds is cancer. Their larger size puts them at an increased risk of osteosarcoma, a type of bone cancer. But don’t fret just yet. These cancers can be treated through chemotherapy and surgery if caught early enough.
While there is little that can be done to prevent this cancer from developing, there are a few things you can do to help catch anything concerning in its early stages.
It is recommended to carry out a physical health check weekly, noting down any abnormalities or behavior changes. These can be done at home and take no more than 10-15 minutes. To do a health check, you want to just inspect their entire body. Get a good look at their face and have a feel of all their limbs.
Another way is to get them to the vet annually, or even bi-annually to do full blood tests. This is so they can pick up on any abnormalities that you’re not able to find doing a regular health check.

Health Conditions For Greyhounds
While Greyhounds are very unlikely to develop any conditions that would greatly shorten or affect their quality of life, they still have a risk of developing some other health conditions due to their anatomy.
Corns
Corns will be noticed as hard and round pieces of skin on your dog’s paws. These can be uncomfortable for them, so it’s ideal to get them to a vet as soon as you find them. These can be found in solely family pets and racing dogs, so it’s most likely caused by a genetic factor.
Bloat
To compensate for their slim stature, Greyhounds have rather small stomachs so are much more susceptible to bloat. Bloat is simply the stomach expanding when full and most of the time it simply will resolve itself over time. If your dog shows signs of extreme discomfort, vomiting and diarrhea then it would be wise to seek a vet’s help.

Hypothermia
Because of a Greyhound’s low body fat percentage, they often have issues regulating temperature. They are much more sensitive to temperature changes, particularly the cold. So, it’s important to keep them warm and toasty come wintertime. It would be wise to invest in a good winter coat for them, something ideally waterproof. This reduces the risk of developing hypothermia when out on walks.
Dental Disease
Dental issues are common for retired racers as the diet they would be commonly fed on was often high in water and allowed a large number of bacteria to build up in the mouth. Potential long-term damage can be prevented by regular teeth brushing and occasional full cleans at the vet.
Conclusion
In summary, Greyhounds are a unique and ancient breed of dog that has been bred for thousands of years for hunting and racing. Greyhounds are such fast and efficient runners because of their unique anatomy, large lung capacity, enormous heart, unique skeletal structure, and powerful hindquarters.
- Pregnant Greyhound: The Stages & How To Care - September 23, 2023
- German Shepherd Whippet Mix: Perfect Blend of Traits and Charisma - August 20, 2023
- Do Italian Greyhounds Like to Cuddle? Unveiling Their Affectionate Nature - August 19, 2023
